Beautiful, Simple and Profound -
Classical Tests of Relativity
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/GR/Week2.html
The Michelson-Morley Experiment In 1887, an exquisitely designed measurement of the earth's motion through the ether results in the most brilliant failure in scientific history. (~27 min) http://www.dailymotion.com/video/x2z733d_the-mechanical-universe-41-the-michelson-morley-experiment_tech
Classical tests of General Relativity https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tests_of_general_relativity#Classical_tests Perihelion precession of Mercury https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tests_of_general_relativity#Perihelion_precession_of_Mercury http://www.relativity.li/en/epstein2/read/i0_en/i1_en/
Deflection of light by the Sun https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tests_of_general_relativity#Deflection_of_light_by_the_Sun
Schwarzschild Calculation - Gravitational deflection of light http://einsteinrelativelyeasy.com/index.php/general-relativity/173-gravitational-deflection-of-light?tmpl=component&print=1 In 1911 the The Equivalence Principle led Einstein to believe that light would be deflected in the presence of a gravitational field. It wasn't until 1915, however, after he had successfully incorporated curved spacetime into a gravitational theory of relativity, that he was able to make an accurate prediction as to the magnitude of such a deflection.
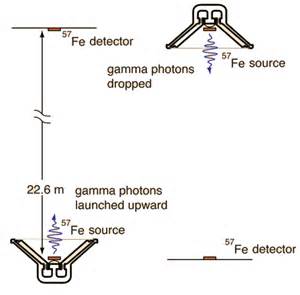
Gravitational redshift of light -- Pound-Rebka experiment http://physics.aps.org/story/v16/st1 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pound-Rebka_experiment http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Relativ/gratim.html#c2 The Pound-Rebka experiment is a well known experiment to test Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity. It is considered to be the experiment that ushered in an era of precision tests of general relativity.
A Clock So Precise It's Beyond Space and Time http://phys.org/news/2014-01-jila-strontium-atomic-clock-precision.htmlNew type of atomic clock keeps time even more precisely https://news.mit.edu/2020/atomic-clock-time-precise-1216 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atomic_clock#Quantum_clocks Atomic clocks are the most precise timekeepers in the world. These exquisite instruments use lasers to measure the vibrations of atoms, which oscillate at a constant frequency, like many microscopic pendulums swinging in sync. The best atomic clocks in the world keep time with such precision that, if they had been running since the beginning of the universe, they would only be off by about half a second today.
Was Einstein Right? A Centenary Assessment http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.7871 http://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.7871v1.pdf The Confrontation between General Relativity and Experiment http://link.springer.com/article/10.12942/lrr-2014-4 lrr-2014-4.pdf Was Einstein Right? 2nd Edition: Putting General Relativity To The Test https://www.amazon.com/Was-Einstein-Right-2nd-Relativity/dp/0465090869 sam.wormley@icloud.com